Let’s learn the steps to check the internet speed on your Ubuntu using the command terminal without using the browser.
Bandwidth describes a range of frequencies in which the transmission of electrical signals is possible. The greater the difference between the lower and higher frequencies, the greater the bandwidth and the more information can be transmitted simultaneously. On the Internet or with a DSL connection, high bandwidth means fast surfing. Conventional ADSL connections (e.g. come at 16 Mbit/s, with VDSL and fiber optic 100 Mbit/s and above are easily achievable. For most applications on the Internet, however, the “slower” bandwidths of 16 Mbit/s /s are also sufficient.
However, there are many web tools that we can easily use to check internet speed. But what if you are using a Linux server with only a command line interface. So here is the solution.
Steps to Check Internet Speed on Ubuntu Linux
1. Perform the system update
Here we will use the APT package manager to update the package index cache and install the latest available updates.
sudo apt update
2. Install Speedtest-cli
By default, there is no command-line supported tool to detect the actual upload and download speed of your internet connection. However, this can be compensated by installing a tool called Speedtest-cli available for installation using Ubuntu’s default system repository.
sudo apt install speedtest-cli
3. Check Internet Speed on Ubuntu Linux
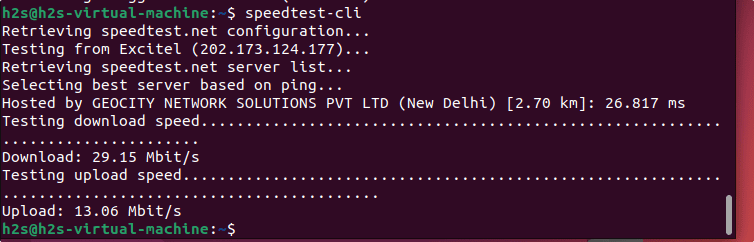
Once the installation of the Speedtest-cli tool is complete, we can call it to retrieve the speed of our Internet connection. Just in your command terminal, type the given command and let it do its job.
speedtest-cli
Wait for a while, the tool will start pinging the nearest server to give the quick result.
The tool is not limited to this, you can also get the resulting CSV format. There are a few options we can work with, here are these:
speedtest-cli --help
usage: speedtest-cli [-h] [--no-download] [--no-upload] [--single] [--bytes]
[--share] [--simple] [--csv]
[--csv-delimiter CSV_DELIMITER] [--csv-header] [--json]
[--list] [--server SERVER] [--exclude EXCLUDE]
[--mini MINI] [--source SOURCE] [--timeout TIMEOUT]
[--secure] [--no-pre-allocate] [--version]
Command-line interface for testing internet bandwidth using speedtest.net.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://github.com/sivel/speedtest-cli
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--no-download Do not perform download test
--no-upload Do not perform upload test
--single Only use a single connection instead of multiple. This simulates a typical file transfer.
--bytes Display values in bytes instead of bits. Does not affect the image generated by --share, nor output from
--json or --csv --share Generate and provide a URL to the speedtest.net share results image, not displayed with --csv
--simple Suppress verbose output, only show basic information
--csv Suppress verbose output, only show basic information in CSV format. Speeds listed in bit/s and not affected
by --bytes
--csv-delimiter CSV_DELIMITER
Single character delimiter to use in CSV output. Default ","
--csv-header Print CSV headers
--json Suppress verbose output, only shows basic information in JSON format. Speeds listed in bit/s and not
affected by --bytes
--list Display a list of speedtest.net servers sorted by distance
--server SERVER Specify a server ID to test against. Can be supplied multiple times
--exclude EXCLUDE Exclude a server from the selection. Can be supplied multiple times
--mini MINI URL of the Speedtest Mini server
--source SOURCE Source IP address to bind to
--timeout TIMEOUT HTTP timeout in seconds. Default 10
--secure Use HTTPS instead of HTTP when communicating with speedtest.net operated servers
--no-pre-allocate Do not pre-allocate upload data. Pre-allocation is enabled by default to improve upload performance. To
support systems with insufficient memory, use this option to avoid a MemoryError
--version Show the version number and exit
Other Items:
• How to Install RPM Packages on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
• How to Install Sysdig on Linux to Monitor System Load
• Install Cinnamon Desktop Environment on Ubuntu 22.04
• How to Install Dolphin File Manager on Ubuntu.